US Debt Ceiling Agreement Reached: The Fiscal Responsibility Act and its Concessions
Student Loans UNpaused
US Debt Ceiling Agreement Reached, Faces Resistance from Both Parties
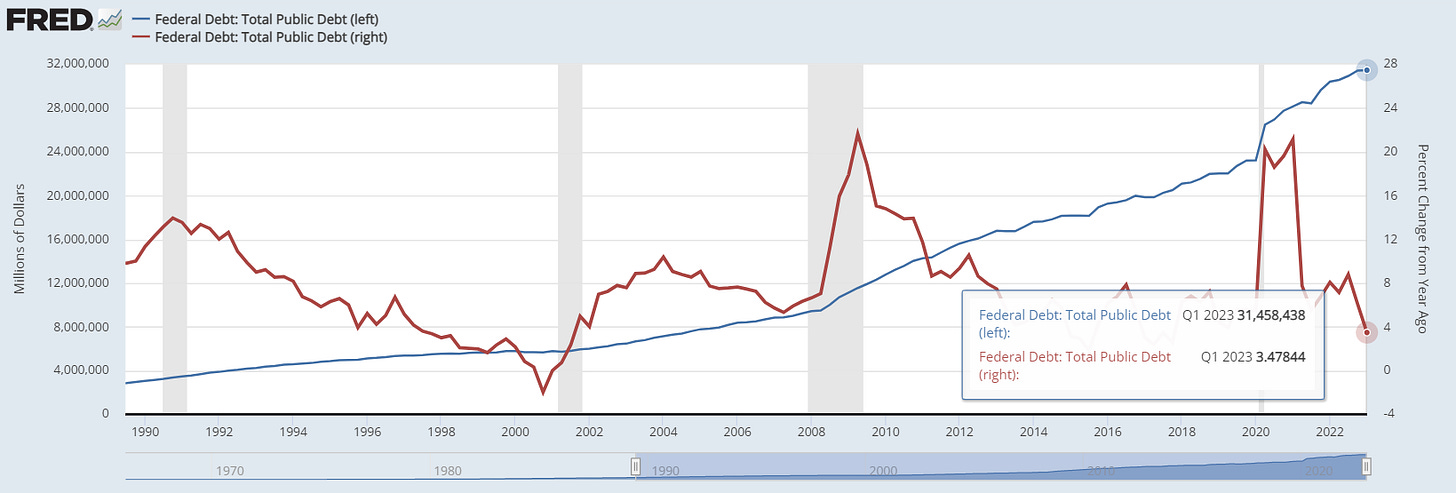
After months of negotiations, an agreement to raise the US debt ceiling has been reached between the Speaker of the House Kevin McCarthy (R-Ca) and the President. The Fiscal Responsibility Act will suspend the debt ceiling for two years until January 2025. The deal includes spending concessions that limit growth in non-essential spending to 0% in fiscal 2024 and just 1% in fiscal 2025.
Despite the agreement, both progressive Democrats and Republicans have expressed dissatisfaction with the terms. Progressive Democrats are unhappy with the inclusion of spending cuts, while Republicans argue that the national debt will reach $35 trillion in 2025 under this deal.
The agreement must pass both chambers of Congress in the coming week, and it is expected to face resistance from lawmakers in both parties. Some Republicans believe the agreement dilutes their party's initial demands, with much of the opposition coming from the right-wing Freedom Caucus. This group includes lawmakers who opposed the Speaker's campaign at the start of the year. However, the Speaker remains optimistic about gaining enough support from his party, stating that 95% of Republican members are excited about the deal. He also anticipates support from some Democrats.
As the official plan has not yet been released, many lawmakers are adopting a wait-and-see approach. Early concerns from conservatives suggest that the compromise does not sufficiently cut future deficits. On the other hand, Democrats worry about proposed changes to work requirements in programs such as food stamps. The agreement represents a compromise, and not everyone will be satisfied with its terms.
The most significant risk to its the agreement passing is that the Speaker will need backing from some Democrats to secure a majority for the bill, but it remains unclear how many will support it. Until the outcome is determined, uncertainty over a potential default in the world's largest economy persists. This uncertainty could impact markets, raise borrowing costs, and damage labor markets globally.
Here are some of the areas of funding that will be impacted by the agreement:
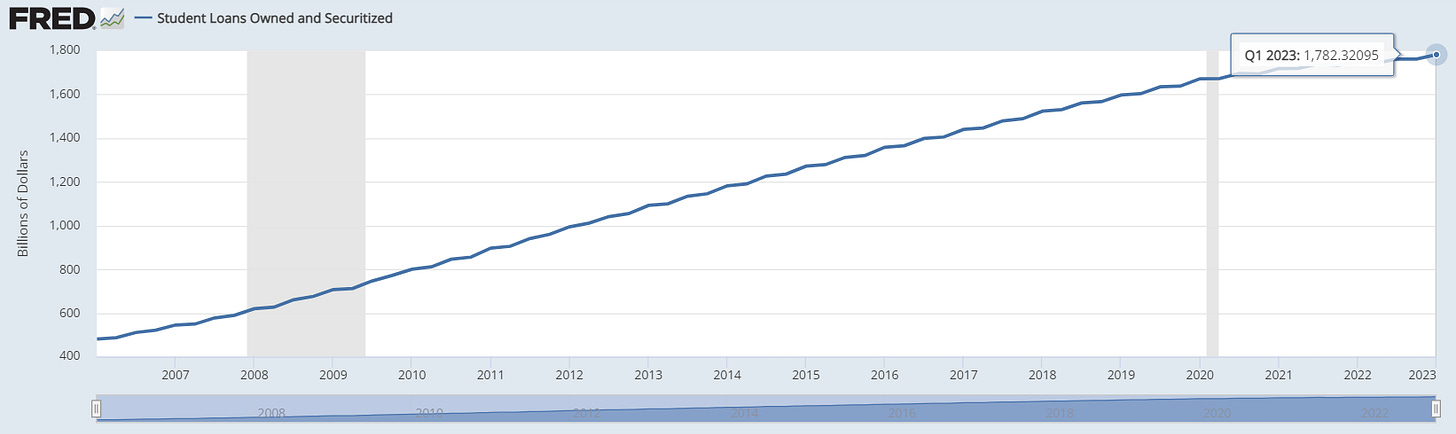
Student Debt UnPaused
House Freedom Caucus members had urged McCarthy to remain steadfast in debt negotiations before Saturday's announcement. However, Democrats firmly opposed the provision, rendering it unacceptable. Under the budget agreement, President Biden's student loan relief measures to forgive $10,000 to $20,000 in debt for nearly all borrowers will remain intact, although the Supreme Court will ultimately make the final decision. Republicans have consistently aimed to scale back the Biden administration's initiatives to provide student loan relief and assistance to millions of borrowers during the pandemic. Biden did agree to end the temporary pause on student loan repayments which will conclude in the last days of August.
Internal Revenue System
As part of the agreement, it has been proposed to rescind $1.5 billion from the $80 billion budget increase allocated to the IRS. Additionally, the package includes strengthening work requirements for certain government assistance programs and reducing a portion of the funding for the IRS.
Medical Care & Covid Fund Clawbacks
The agreement includes some additional provisions that involve taking back funds from certain programs. For example, $400 million would be taken back from the CDC Global Health Fund, and $1.5 billion would be taken back from the Vaccine Distribution and Monitoring Program. However, there are exceptions for important areas like veterans' medical care, housing assistance, and a program focused on developing COVID-19 vaccines and treatments.
There is a commitment to fully fund medical care for veterans based on the levels proposed in President Biden's 2024 budget blueprint. It also includes a dedicated fund for veterans who have been exposed to harmful substances or environmental hazards.
The proposal to introduce work requirements for some Medicaid recipients faced strong opposition from the White House and congressional Democrats. They argued that it would make it harder for people to afford food or healthcare without actually increasing employment. As a result, this proposal was ultimately not included in the final agreement.
Additionally, approximately $30 billion in unspent coronavirus relief funds, approved in previous bills, would be rescinded. This would involve taking back unused money from various federal programs that received aid during the pandemic, such as rental assistance, small business loans, and rural broadband.
SNAP
The agreement aims to increase the number of work requirements for SNAP, which is the program previously known as food stamps. However, the changes being proposed are less extensive compared to what was included in the debt ceiling bill passed by the House. Currently, most adults who are physically capable and aged between 18 and 49 already have work requirements in place. The new bill would gradually raise the age limit, so by 2025, the maximum age for work requirements would be 54.
Environment & Green Energy
The final deal does not include the Republican proposal to eliminate a lot of the clean energy tax credits that Democrats approved last year through party-line votes. These tax credits were meant to encourage the production and use of clean energy. Instead, the deal introduces changes to the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) for the first time in almost forty years. These changes involve appointing a single lead agency responsible for conducting and organizing environmental reviews, with the aim of making the process more efficient. Additionally, the deal simplifies certain requirements for environmental reviews, such as setting limits on the length of environmental assessments and impact statements.
2024 Election
The dispute regarding the debt ceiling not only has implications for the economy and finances but could also affect the race for the presidency. President Biden has already started his campaign for re-election, while former President Trump and Governor Ron DeSantis of Florida are the leading candidates for the Republican nomination. Republicans are expressing dissatisfaction with the initial agreement on the debt ceiling between President Joe Biden and House Speaker Kevin McCarthy.
For more analysis on these topics, check out these articles:
Rabobank: Will The Debt Deal Pass Smoothly Or Will Congress Spoil It In The Last Minute?
Debt ceiling deal: Whats in, whats out of the bill to avert US default
FirstFT: House Speaker McCarthy faces Republican revolt as US default deadline looms
Surrender: Chorus of Republicans Disappointed With Debt Ceiling Agreement
White House reaches deal with Republicans to avert US debt default
All Major Congress Leaders Signal Support for Debt Ceiling Bill Despite Backlash
Dollar Nudges Lower as US Debt Ceiling Deal Dents Safe-Haven Appeal
House Freedom Caucus Republicans Sound Alarm on Debt Ceiling Agreement
Thanks For Reading!
If you find value in this newsletter and want to make sure you don't miss any important updates, you should definitely consider subscribing. By subscribing, you'll be the first to know about new articles and special offers.
If you have any newsletters you wish to see in our lineup, please reach out and let us know. We will continually look to incorporate more sources to our weekly wrap-up.